Table of Content
1. Purpose
2. Scope
3. References
4. Definitions and Abbreviations
5. Responsibilities
6. Procedure
6.1 Risk Assessment
6.2 Medical Screening & Treatment
6.3 Health Surveillance
6.4 Incident Investigation
6.5 Registered Medical Practitioner
6.6 Rehabilitation
6.7 Control Measures
7. Records
8. Appendix
1. Purpose
This procedure describes the requirements for managing workplace conditions and work activities to safeguard against adverse effects on worker’s health.
Where there is a known risk or potential for work-related/occupational ill-health/disease, controls will be established and workers’ will be monitored through a health surveillance program.
2. Scope
This procedure applies to all employees and assistance will be provided to subcontractors to manage the health of their employees.
3. References
- HSE Risk Management Procedure
- HSE Accidents and Incidents Procedure
- Work-Related/Occupational Injury and illness/Disease Management Procedure
4. Definitions and Abbreviations
Health Screening:
Is a procedure that is performed to detect the presence of a specific medical condition, which generally does not present any symptoms. Health screening involves a medical examination, medical tests and gathering health related information about a person.
Work-Related/Occupational Health Surveillance:
Is the monitoring of workers to detect signs or symptoms of work-related/occupational ill-health/disease so that steps can be taken to eliminate or reduce the likelihood of work related/occupational ill-health/disease? It also evaluates the effectiveness of controls and provides an opportunity to reinforce specific preventative measures.
5. Responsibilities
- Project Director
- Registered Medical Practitioner
6. Procedure
6.1 Risk Assessment
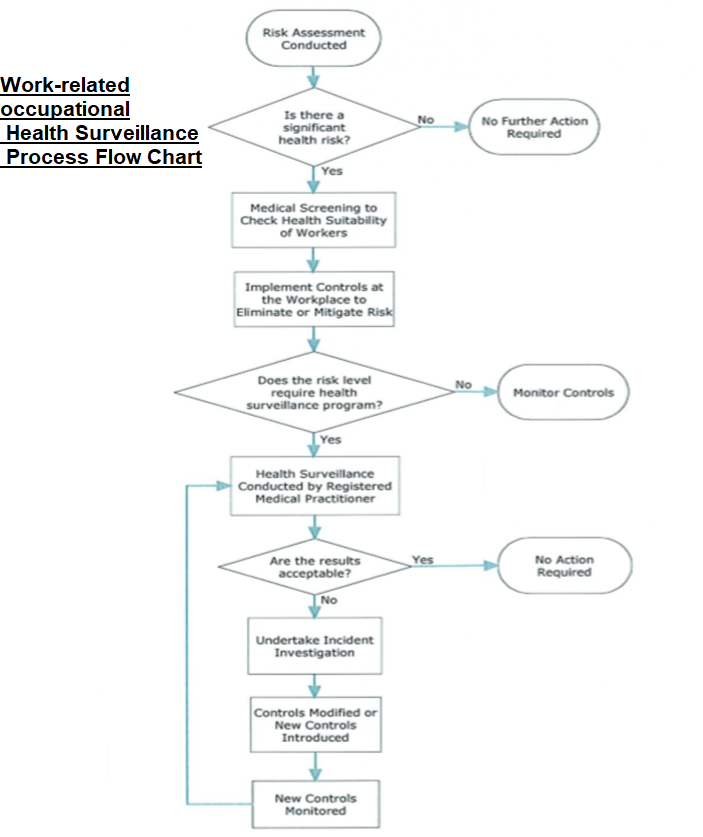
Prior to mobilizing workers to a project, a risk assessment shall be conducted to ascertain the health risks likely to be encountered in working and/or living in the particular region of the world where the project is located.
Factors to be considered include work:
- At high altitude (greater than 2,500 meters above sea level);
- In remote locations;
- On-board a vessel at sea;
- In extreme climatic conditions;
- In malaria or other disease prone areas ;
- In a pressurized working environment (e.g. pressurized tunneling).
The Project director is responsible to ensure that the project risk assessment includes workplace exposures which represent significant risks to workers’ health. Refer to HSE Risk Management procedure.
6.2 Medical Screening/Treatment
If the need is identified in the risk assessment, individuals working on the project shall be screened to ensure they are suitable to work safely in known high risks conditions.
Screening shall be carried out regardless of whether they are new employees, transferred from another project or sub-contractor’s employees.
Where the identified health risks can be mitigated through medication and/or inoculations, these shall be administered by a Registered Medical Practitioner prior to the employee’s departure to the project.
6.3 Health Surveillance
The following criteria should be considered as a requirement for determining the need to conduct health surveillance:
- There is an identifiable disease or other identifiable adverse health outcome;
- The disease or health effect may be related to exposure;
- iii. There is a likelihood that the disease or health effect may occur;
- iv. There are valid techniques for detecting indications of the disease or health effects;
- v. Exposure to chemical hazards such as: hazardous substances;
- Exposure to fumes, vapors, dust etc. and/or
- Exposure to physical hazards such as: noise, vibration, asbestos, lead, UV radiation, ionizing radiation.
Additional advice should be sought from a Registered Medical
6.4 Incident Investigation
Where results from the health surveillance indicate that workplace control measures may have failed, the Project Director will arrange for an incident investigation to be undertaken immediately, as required by the procedure of HSE Accidents and Incidents.
6.5 Registered Medical Practitioner
A Registered Medical Practitioner shall be engaged for medical screening and health surveillance. The health surveillance shall be conducted at intervals recommended by the Registered Medical Practitioner. The Registered Medical Practitioner should retain the medical records of workers and make them available on request to the HR Director/Manager and to the workers who have undergone medical surveillance. Records retained will be securely kept and remain strictly confidential.
6.6 Rehabilitation
Should an employee suffer ill-health/disease caused by exposure at the workplace, company will provide the necessary assistance to rehabilitate the employee to a level of health to enable return to work. Refer to procedure for Work-Related/Occupational Injury and Illness/Disease Management.
6.7 Control Measures
It is important to understand that health surveillance is not considered a control against exposure to health hazards, but as a means to confirm that the control measures are working. Selection of control measures to eliminate or mitigate potential health hazards, should follow the control hierarchy described in HSE Risk Assessment procedure.
7. Relevant Records
Risk Assessment Records
8. Appendix
Appendix A- Work-related/occupational Health Surveillance Process Flow Chart